JDK动态代理代理与Cglib代理原理探究
一、前言
Java中常见的代理有JDK代理和Cglib代理,无论是AOP实现还是mybaits动态生成数据库操作类无一不是通过代理来搞的,下面讲解下原理以及比较
二、JDK代理
2.1 试验测试
接口类:
public interface UserService {
public abstract void add();
}
实现类:
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public void add() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("--------------------add----------------------");
}
}
InvocationHandler类
public class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object target;
public MyInvocationHandler(Object target) {
super();
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
PerformanceMonior.begin(target.getClass().getName()+"."+method.getName());
//System.out.println("-----------------begin "+method.getName()+"-----------------");
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
//System.out.println("-----------------end "+method.getName()+"-----------------");
PerformanceMonior.end();
return result;
}
public Object getProxy(){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
//生成的代理类保存到磁盘
System.getProperties().put("sun.misc.ProxyGenerator.saveGeneratedFiles", "true");
UserService service = new UserServiceImpl();
MyInvocationHandler handler = new MyInvocationHandler(service);
UserService proxy = (UserService) handler.getProxy();
proxy.add();
}
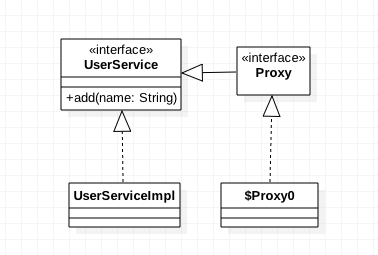
UserServiceImpl被JDK代理后的类,在项目的com.sun.proxy下面生成$Proxy0.class类
package com.sun.proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException;
import proxy.JDK.UserService;
public final class $Proxy0
extends Proxy
implements UserService
{
private static Method m1;
private static Method m3;
private static Method m0;
private static Method m2;
public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler)
{
super(paramInvocationHandler);
}
public final void add()
{
try
{
//第一个参数是代理类本身,第二个是实现类的方法,第三个是参数
this.h.invoke(this, m3, null);
return;
}
catch (Error|RuntimeException localError)
{
throw localError;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(localThrowable);
}
}
...
static
{
try
{
m3 = Class.forName("proxy.JDK.UserService").getMethod("add", new Class[0]);
...
return;
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException localNoSuchMethodException)
{
throw new NoSuchMethodError(localNoSuchMethodException.getMessage());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException localClassNotFoundException)
{
throw new NoClassDefFoundError(localClassNotFoundException.getMessage());
}
}
}
也就是说main函数里面的proxy实际就是$Proxy0的一个实例对象。
可知JDK动态代理是使用接口生成新的实现类,实现类里面则委托给InvocationHandler,InvocationHandler里面则调用被代理的类方法。
2.2 源码分析
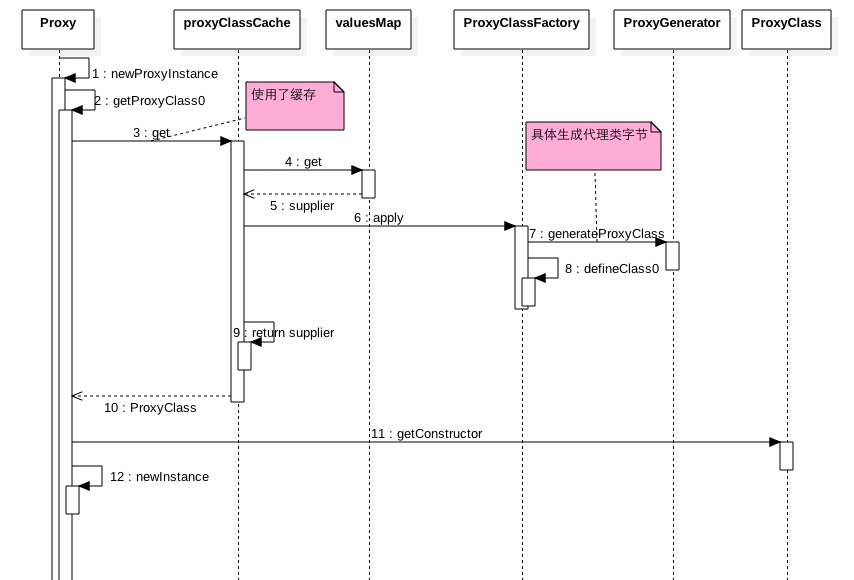
如时序图首先调用了newProxyInstance方法:
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
...
/*
* 查找或者生成代理类的大class类.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);
/*
*
使用代理类构造函数实例化一个对象
*/
try {
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (sm != null && ProxyAccessHelper.needsNewInstanceCheck(cl)) {
// create proxy instance with doPrivilege as the proxy class may
// implement non-public interfaces that requires a special permission
return AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
public Object run() {
return newInstance(cons, ih);
}
});
} else {
return newInstance(cons, ih);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString());
}
}
然后看下关键函数getProxyClass0
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// 使用缓存,如果缓存中存在由实现类加载器创建的代理类,则直接返回,否者使用ProxyClassFactory创建代理类的Class
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
在看下ProxyClassFactory的apply函数:
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
...
/*
* Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
* 根据接口类生成代理类.
*/
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
...
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
三、Cglib代理
3.1 试验测试
测试代码
public void testCglibProxy() {
//生成代理类到本地
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "/Users/zhuizhumengxiang/Downloads");
UserServiceImpl service = new UserServiceImpl();
CglibProxy cp = new CglibProxy();
UserService proxy = (UserService) cp.getProxy(service.getClass());
proxy.add();
proxy.sub();
proxy.hello("zlx");
proxy.service("zlx");
proxy.toString();
}
MethodInterceptor类:
public class CglibProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
private Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
public Object getProxy(Class clazz) {
enhancer.setSuperclass(clazz);
enhancer.setCallback( this);
//enhancer.setCallbackType(clazz);;
return enhancer.create();
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
PerformanceMonior.begin(obj.getClass().getName()+"."+method.getName());
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
// Object result = method.invoke(obj, args);
PerformanceMonior.end();
return result;
}
}
生成的代理类反编译后:
package proxy.JDK;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
public class UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$a68ccf10
extends UserServiceImpl
implements Factory
{
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static final Method CGLIB$add$0$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$add$0$Proxy;
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$service$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$service$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$testAnnotaion$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$testAnnotaion$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$testAnnotaion2$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$testAnnotaion2$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hello$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hello$4$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$sub$5$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$sub$5$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$finalize$6$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$finalize$6$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$7$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$7$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$8$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$8$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$9$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$9$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$10$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$10$Proxy;
...
final void CGLIB$add$0()
{
super.add();
}
public final void add()
{
MethodInterceptor tmp4_1 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (tmp4_1 == null)
{
tmp4_1;
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
if (this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 != null) {
return;
}
super.add();
}
...
public UserServiceImpl$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$a68ccf10()
{
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(paramArrayOfCallback);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = paramArrayOfCallback;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object paramObject)
{
a68ccf10 locala68ccf10 = (a68ccf10)paramObject;
if (!locala68ccf10.CGLIB$BOUND)
{
locala68ccf10.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
Object tmp23_20 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (tmp23_20 == null)
{
tmp23_20;
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
}
locala68ccf10.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (tmp31_28 == null ? tmp31_28 : (MethodInterceptor)((Callback[])tmp23_20)[0]);
}
}
public Object newInstance(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(paramArrayOfCallback);
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new a68ccf10();
}
public Object newInstance(Callback paramCallback)
{
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(new Callback[] { paramCallback });
CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(null);
return new a68ccf10();
}
public Callback getCallback(int paramInt)
{
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
switch (paramInt)
{
case 0:
break;
}
return null;
}
public void setCallback(int paramInt, Callback paramCallback)
{
switch (paramInt)
{
case 0:
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = ((MethodInterceptor)paramCallback);
break;
}
}
public Callback[] getCallbacks()
{
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
return new Callback[] { this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 };
}
public void setCallbacks(Callback[] paramArrayOfCallback)
{
this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = ((MethodInterceptor)paramArrayOfCallback[0]);
}
static {}
}
Cglib是通过直接继承被代理类,并委托为回调函数来做具体的事情:
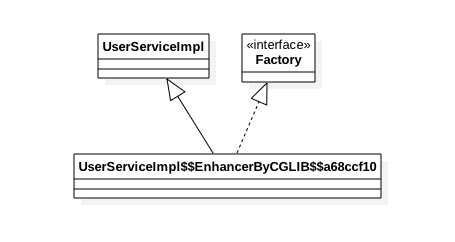
从代理类里面可知道对于原来的add函数,代理类里面对应了两个函数分布是add 和CGLIB$add$0
其中后者是在方法拦截器里面调用的的,前者则是我们使用代理类时候调用的函数。当我们代码调用add时候,会具体调用到方法拦截器的intercept方法,该方法内则通过proxy.invokeSuper调用CGLIB$add$0
3.2 源码分析
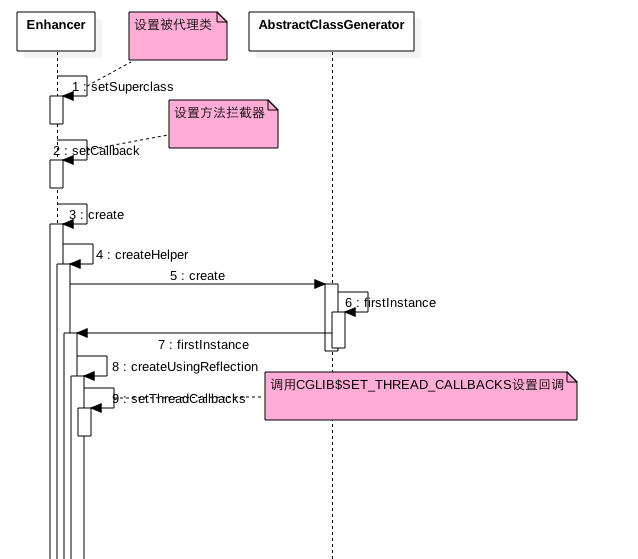
如图首先设置被代理类,然后设置自己写的方法拦截器,然后创建创建代理类的Class对象,并调用代理类的CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS方法设置回调。
四、总结
对应JDK动态代理机制是委托机制,具体说动态实现接口类,在动态生成的实现类里面委托为hanlder去调用原始实现类方法。
比如接口类为Abo,实现类为AboImpl,AboImpl的代理类为$ProxyAoImpl ,那么$ProxyAoImpl 能赋值给Abo?能够赋值给AboImpl?
$ProxyAoImpl 是能够赋值给Abo的,因为前者间接实现了后者,但是$ProxyAoImpl 不能赋值给AboImpl因为他们没有继承或者实现关系。所以回顾下自己项目中Rpc里面autowired时候都是对bo类进行的,而不是对boimpl,并且我们的boimpl类一般都是配置了事务切面被代理过的。
对应Cglib则使用的继承机制,具体说被代理类和代理类是继承关系,所以代理类是可以赋值给被代理类的,如果被代理类有接口,那么代理类也可以赋值给接口。
另外JDK代理只能对接口进行代理,Cglib则是对实现类进行代理。
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自并发编程网 – ifeve.com本文链接地址: JDK动态代理代理与Cglib代理原理探究

 (5 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)
(5 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)

为啥不能评论了那?
第一次评论